|
Getting your Trinity Audio player ready...
|
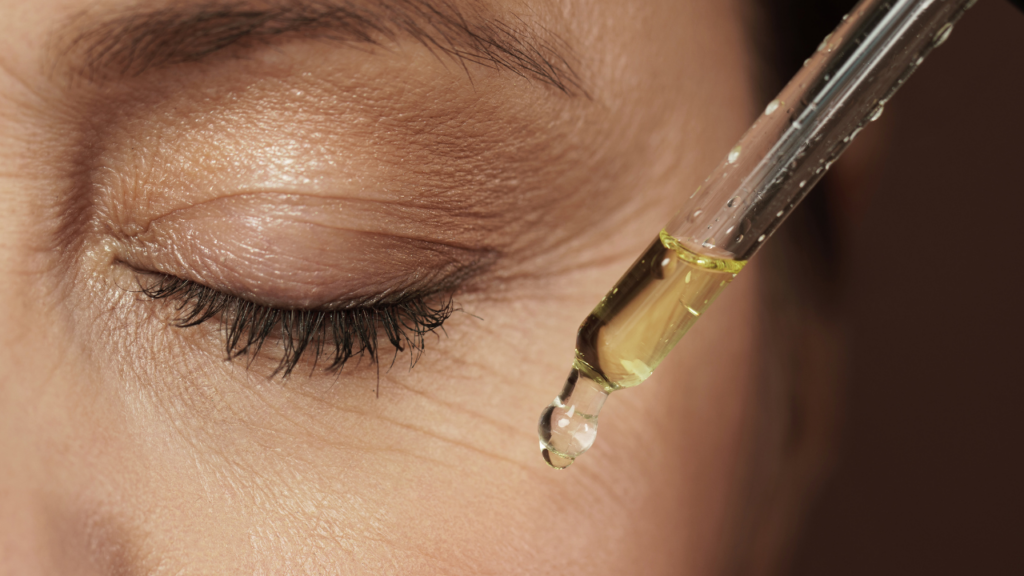
The search for effective anti-aging products and treatments often leads to peptides, a significant class of ingredients in the skincare industry. With the potential to diminish the signs of aging and enhance skin health, peptides are becoming a stalwart on the shelves of individuals looking to preserve their skin’s youthfulness. This article delves into the science behind peptides, their role in anti-aging, their applications in skin care, and the benchmarks for their safe usage.
The Role of Peptides in Anti-Aging
Peptides are short strings of amino acids that serve as the building blocks for proteins—vital components of the skin’s structure. Within the scope of anti-aging, peptides are valued for their properties that contribute to rejuvenating aged skin.
They play a role in modulating various cellular processes that influence the extracellular matrix (ECM) integrity and the synthesis of ECM proteins like collagen, laminin, and elastin, which are important in maintaining the skin’s firm, pliable, and youthful appearance.
Understanding Skin Aging and Basement Membrane
A significant aspect of skin aging involves changes in the dermal-epidermal junction (DEJ), including the basement membrane’s functionality. DEJ is an important site of attachment in the skin.
One of the primary causes of skin aging is when nidogens, collagen IV, and other core peptides integral to this structure experience reduced expression, disturbing the signaling between epidermal keratinocytes and dermal fibroblasts.
This weakened communication can result in diminished collagen synthesis, leading to the loss of skin elasticity and the appearance of wrinkles. Therefore, targeting the DEJ and boosting its core components is a primary strategy in many anti-aging regimens.

Anti-Aging Benefits of Peptides
Stimulating Collagen for Skin Tightening
Peptides, such as matrixyl, act as messengers that encourage skin cells to undertake collagen production. This is vital for sustaining skin firmness and minimizing the clinical features of aging. These agents can invoke increased collagen synthesis, aiding in the reduction of visible skin wrinkles and sustaining the integrity of the dermal layer.
Improving Skin Proteins and Anti-Wrinkle Effects
Certain peptides also have a notable effect on the expression of essential skin proteins such as laminins and integrins. For example, a specific peptide, tripeptide-29, has been shown to have significant anti-wrinkle effects due to its influence on collagen XVII and other components related to the basal lamina. By supporting the structure of the extracellular matrix and preventing its degradation through matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs), peptides exhibit powerful anti-aging strategies.
Hydration and Complexion Improvement
By promoting dermal fibroblast activity and ECM protein synthesis, peptides help maintain optimal hydration levels. Some peptides also enhance the natural extracts’ bioavailability, allowing for better nutrient uptake and a more radiant complexion.
Core Peptides in Anti-Aging Treatments
Epitalon
Used to stimulate the pineal gland, the peptide epitalon has been claimed to have systemic anti-aging effects by influencing telomerase activity and promoting NAD+ synthesis—these are factors that affect cellular energy and may extend the lifespan of skin cells.
GHK-Cu
GHK-Cu, a copper complex peptide, is recognized for its ability to improve the appearance of aged skin. It facilitates the binding of copper ions, which are essential in various enzymatic processes that tighten the skin, clarify complexion, and enhance wound healing.
Argireline
As a synthetic hexapeptide, argireline is a popular inclusion for its ability to minimize the prominence of wrinkles, mimicking the effects of Botox without invasive procedures. It operates by disrupting the signaling pathways that lead to muscle tension, thereby reducing fine lines caused by repetitive facial expressions.
Matrixyl
Matrixyl, another core ingredient in peptide-based anti-aging treatments, helps to improve the levels of several important types of collagen and hyaluronic acid in the skin. Its use is tied to reports of significant improvements in skin texture and a reduction in wrinkle depth over time.
Foxo4-dri
FOXO4-DRI is a peptide compound that has gained attention in the field of anti-aging research. Its potential lies in targeting and disrupting interactions between proteins involved in cellular senescence, a process where cells lose their ability to divide and function properly as they age.
By interfering with these interactions, FOXO4-DRI may help remove senescent cells from the body. This removal of aged cells could potentially delay age-related health issues and contribute to a more youthful and healthier aging process. However, it’s important to note that further research is needed to fully understand the safety and effectiveness of FOXO4-DRI in anti-aging applications.
Safe Use of Peptides in Anti-Aging Skincare
Despite their many benefits, peptides must be used carefully within anti-aging skincare routines. Prioritizing solutions that ensure the stability and bioavailability of peptides is crucial—penetrating the skin’s barrier to reach the living cells where they can enact their anti-aging effect. It’s important to select products that are backed by robust research and clinical studies, which confirm their safety and efficacy for long-term use on the face and other sensitive areas prone to aging, such as the neck area.
Conclusion
In conclusion, peptides play a vital role in anti-aging skincare by promoting collagen production, improving skin proteins, and enhancing hydration and complexion. They offer a range of benefits for maintaining youthful skin and addressing the signs of aging.
However, it’s essential to choose products with stable and bioavailable peptides supported by research and clinical studies to ensure their safe and effective use in your skincare routine. With the right approach, peptides can be a valuable addition to your anti-aging regimen, helping you achieve a more radiant and youthful complexion.
Nevertheless, it’s important to remember that some peptides have yet to been approved by the FDA.
FAQ
What are peptides and how do they work for anti-aging?
Peptides are short chains of amino acids that can boost collagen production, improve skin hydration, and reduce wrinkles when applied topically in anti-aging skincare products. They work by stimulating various skin processes that promote a more youthful and healthy complexion.
Are peptides safe to use for anti-aging?
Peptides are generally safe to use for anti-aging when included in skincare products. They have a low risk of causing adverse reactions and can offer several benefits for improving skin texture, reducing wrinkles, and promoting a more youthful appearance. However, the consumer should still ensure that the treatments are backed by research and clinical trials to ensure safety.
What are the benefits of using peptides for anti-aging?
Using peptides for anti-aging can enhance collagen production, reduce wrinkles, improve skin hydration, protect against oxidative damage, and promote a smoother complexion, contributing to a more youthful appearance.
How should I incorporate peptides into my anti-aging skincare routine?
Incorporate peptides into your anti-aging skincare routine by using products like serums, creams, or moisturizers containing peptides. Apply them after cleansing and toning but before sunscreen or moisturizer. Follow the product’s instructions and consult a dermatologist for personalized guidance.
Are there any side effects of using peptides for anti-aging?
Peptides used in skincare products typically have a low risk of side effects. However, some individuals may experience mild irritation or allergic reactions. Perform a patch test and consult with a dermatologist if you have concerns about sensitivity.
Disclaimer: Please note that many peptide therapies are not FDA-approved and their efficacy and safety have not been fully established. It is crucial to consult with your healthcare provider before starting any new supplements or treatments, including peptide therapy.
References
Sidbury, Robert. “Newborn Skin Development: Structure and Function.” Avery’s Diseases of the Newborn, 2024. https://doi.org/10.1016/b978-0-323-82823-9.00091-x. https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/medicine-and-dentistry/dermoepidermal-junction
Khavinson, V. Kh., I. E. Bondarev, and A. A. Butyugov. Bulletin of Experimental Biology and Medicine 135, no. 6 (2003): 590–92. https://doi.org/10.1023/a:1025493705728. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12937682/
Bae, Soon-Min & Ahn, Yong-Hoon & Jung, Jin-Kyo & Hwang, Jeong-Geun. (2010). A Study on the Skin Anti-wrinkle Effect of Novel Palmitoyl Tripeptide. Journal of the Society of Cosmetic Scientists of Korea. 36. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/264182749_A_Study_on_the_Skin_Anti-wrinkle_Effect_of_Novel_Palmitoyl_Tripeptide
Pickart, Loren, and Anna Margolina. “Regenerative and Protective Actions of the GHK-Cu Peptide in the Light of the New Gene Data.” International Journal of Molecular Sciences 19, no. 7 (July 7, 2018): 1987. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19071987. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6073405/
Wang, Yuan, Mei Wang, Shengxiang Xiao, Ping Pan, Ping Li, and Jia Huo. “The Anti-Wrinkle Efficacy of Argireline, a Synthetic Hexapeptide, in Chinese Subjects.” American Journal of Clinical Dermatology 14, no. 2 (February 16, 2013): 147–53. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40257-013-0009-9. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23417317/
Griffiths, Tamara W, Rachel E Watson, and Abigail K Langton. “Skin Ageing and Topical Rejuvenation Strategies.” British Journal of Dermatology 189, no. Supplement_1 (October 2023): i17–23. https://doi.org/10.1093/bjd/ljad282. https://academic.oup.com/bjd/article/189/Supplement_1/i17/7333865
Huang, Yuzhao, Yuchen He, Meagan J. Makarcyzk, and Hang Lin. “Senolytic Peptide FOXO4-Dri Selectively Removes Senescent Cells from in Vitro Expanded Human Chondrocytes.” Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology 9 (April 29, 2021). https://doi.org/10.3389/fbioe.2021.677576. https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fbioe.2021.677576



Wow, this is a really comprehensive and informative article on peptides and their role in anti-aging skincare! It’s fascinating to learn about how peptides, as short chains of amino acids, can have such a significant impact on skin health, especially in maintaining youthfulness and reducing the signs of aging.
I particularly appreciate how the article dives into the science behind it all, explaining how peptides stimulate collagen production and improve skin proteins, which are key to reducing wrinkles and maintaining skin elasticity. It’s interesting to learn about different types of peptides like Matrixyl, Argireline, and GHK-Cu, and their specific benefits. The mention of FOXO4-DRI and its potential in targeting cellular senescence is particularly intriguing, although it’s good to know that more research is needed in this area.
It’s also great that the article emphasizes the importance of choosing peptide products that are backed by research and clinical studies. With so many products on the market, it can be overwhelming to choose the right one, but understanding the science behind these ingredients definitely helps make more informed decisions.
I’m curious to know more about the long-term effects of using peptide-based products and whether there are any particular combinations of ingredients that work best with peptides. Also, it would be interesting to learn about any advancements in peptide research that might lead to even more effective anti-aging treatments in the future.
Thanks for sharing such an insightful article! It’s really helpful for anyone looking to understand the role of peptides in skincare and how to integrate them into an anti-aging routine.